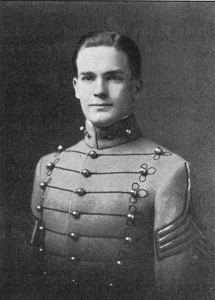
Cann Memorial Hall was dedicated in February, 1965. At the time, Cann housed 86 Rooks (freshmen Cadets) and a small cadre of upperclassmen. The dormitory was named in honor of George Turner Cann, PMC 1885. The dedication ceremony was attended by faculty, Cadets and honored guests of PMC, including Cadet Captain Walter Clayton Jr., President of the Board of Trustees, Laurence Sharples, and Cann family members. In accepting the dormitory, it was said Cann “certainly was not ordinary.”
Judge Cann’s forebears settled in Georgia shortly after James Oglethorpe founded the colony in 1732. He was the valedictorian of his high school class in 1882 and entered Pennsylvania Military Academy in the fall. After only three years, he earned the distinction of being Cadet Captain, achieved the highest grade average (99.7 on the Merit List) ever attained at PMA, and became the class valedictorian. After graduation he attended Columbia University where he continued his studies and received his diploma from the law school. He returned to Savannah and was admitted to the bar. His law career included three terms as county attorney and as judge of the Eastern Judicial Circuit Court of Georgia.
 George Cann was an active participant in many civic and fraternal organizations, including the Savannah Board of Trade, the Georgia Historical Society, and Director of the YMCA. In 1887, he joined the Savannah Volunteer Guards as a private. He advanced quickly, however, and attained the rank of captain of Company C. He was a skilled marksman and led Company C at the sixth annual New Jersey Riflemen tournament at Sea Girt, NJ. In 1896. Cann won the Wimbledon Cup with a score of 103 of of a possible 150.
George Cann was an active participant in many civic and fraternal organizations, including the Savannah Board of Trade, the Georgia Historical Society, and Director of the YMCA. In 1887, he joined the Savannah Volunteer Guards as a private. He advanced quickly, however, and attained the rank of captain of Company C. He was a skilled marksman and led Company C at the sixth annual New Jersey Riflemen tournament at Sea Girt, NJ. In 1896. Cann won the Wimbledon Cup with a score of 103 of of a possible 150.
In 1924, Judge Cann conferred the degree of Bachelor of Military Science upon 64 PMC alumni. Judge Cann explained that “the degree was designed to honor graduates of PMC who had served in any branch of the military in time of actual warfare.” He went on to say that PMC
creates a sound body and healthy mind, teaches obedience ot law and authority and inspires lofty ideals. PMC men have been heroes in peace and in war. They are always ready to make the supreme sacrifice when their country calls them.
Throughout his life Judge Cann continued his involvement with PMC. He was a member of the Board of Trustees from 1924-1937 and was awarded the Honorary Degrees of Master of Arts in 1892 and Doctor of Laws in 1935.